As network technologies have advanced, CBRS — which stands for
Citizens Broadband Radio Service — has become a trending topic in the telecommunications (telecom) space. Put simply, CBRS is a spectrum of radio frequencies that are suitable for deploying
4G LTE and 5G networks.
As a result, organizations that depend on high-speed wireless connectivity are particularly eager to take advantage of CBRS's previously restricted frequency band to build private LTE networks.
The industries and use cases that stand to benefit from the security and reliability of private networsk are broad, and include healthcare, manufacturing,
agriculture, educational facilities, smart cities, retail, warehousing and supply chain, and industrial operations.
In this post, we’ll explain more about how CBRS is enabling the development of private LTE networks today. We’ll also explore:
- Why enterprises are investing in building private LTE networks
- What to look for when considering private LTE network providers
- Which industries are already implementing use cases for private LTE
What Is CBRS?
Also known as the 3.5 GHz band or LTE band 48, CBRS represents radio frequencies from 3.5 GHz to 3.7 GHz. In the past, CBRS was only accessible to the U.S. federal government and fixed satellite services, but as of 2019, the “innovation band” became partially available for commercial use.
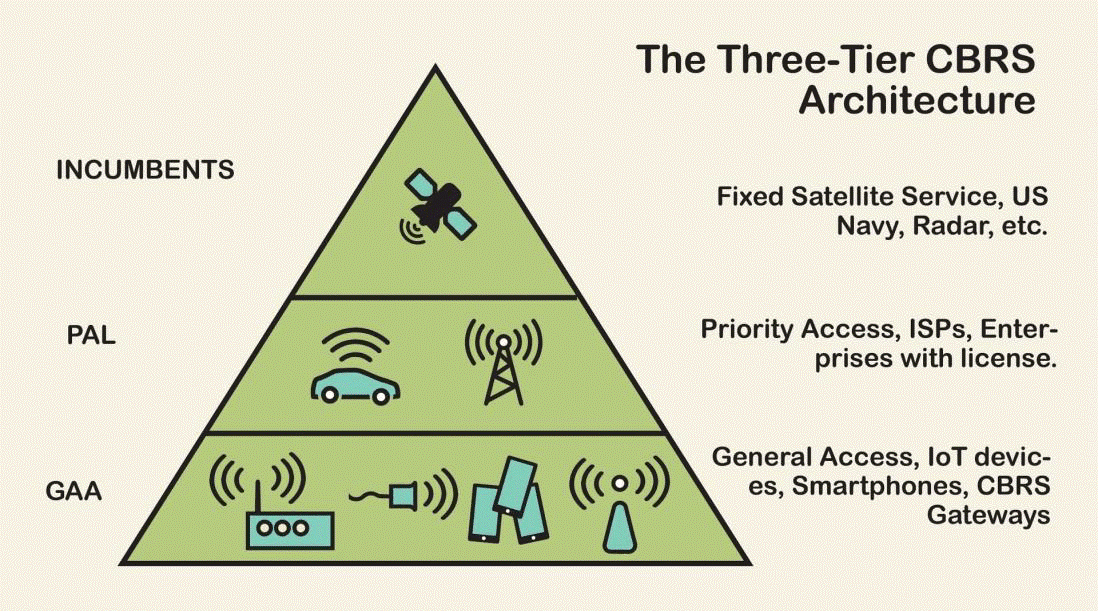
To protect mission-critical use cases, the FCC implemented a shared spectrum model for CBRS usage. Access to the CBRS spectrum is managed across three groups:
- Tier 1 — reserved for incumbent users (primarily the U.S. Navy and satellite ground stations).
- Tier 2 — available for enterprise users with priority access licenses (PALs).
- Tier 3 — open to general authorized users (GAA) at no cost.
Industry observers have said that “CBRS will put enormous wireless networking power into the hands of organizations.” With private LTE networks, enterprises will be able to extend — and in some cases replace — the public 4G and 5G networks that lack the needed performance and reliability for today’s most advanced wireless use cases.
What Is Private LTE?
We’ve discussed the impact of CBRS licensing — but what is a private cellular network and why should enterprises care?
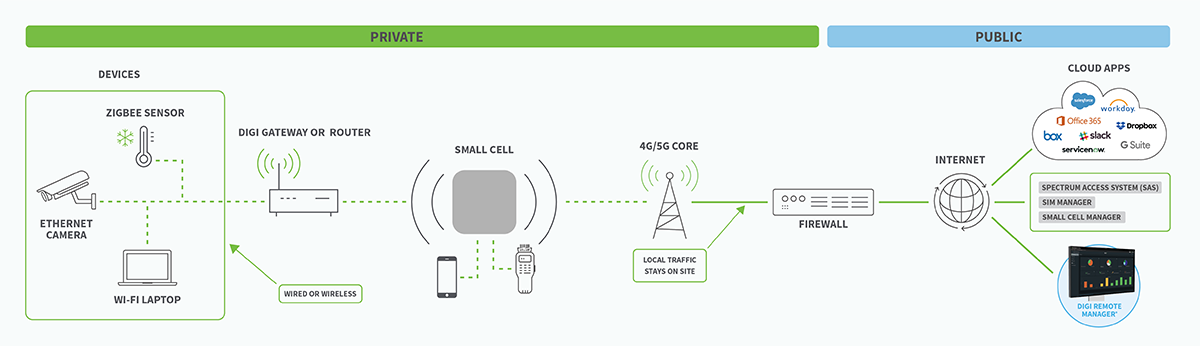
A private LTE network uses small cells, conceptually similar to Wi-Fi access points, to stand up a dedicated private wireless network that can cover tens of thousands of square feet — a smaller scale version of a public cellular network. Establishing an independent LTE network requires more time and resources than relying on existing public networks.

Private LTE vs Public LTE
You might wonder — why turn to private networks at all? After all, public LTE and Wi-Fi networks have become a necessity and even an expectation in modern-day life. Why are enterprises investing in building their own networks when they could take advantage of the networks that telecom giants have already built out?
For many enterprise organizations, wireless has become the “fourth utility” — a resource that’s as vital as power, water and Internet connectivity.
When public LTE and Wi-Fi networks aren’t available due to coverage limitations or aren’t working well because of capacity issues, data-driven operations and critical services grind to a halt.
To overcome this challenge, organizations in the U.S. are increasingly looking at the option of CBRS-based private cellular networks to meet their business connectivity needs. There are three common scenarios where public LTE and Wi-Fi are not ideal — when networks:
- Have coverage limitations and don’t extend to the site in question.
- Are not working well or are transmitting data slowly due to high levels of traffic.
- Do not meet the appropriate security requirements for the application, use case or industry.
Private LTE vs Wi-Fi
While the underlying concepts and architecture of LTE and Wi-Fi networks are similar, the experience of using these two wireless technologies is quite different. Let's discuss the key differences in performance and security.

LTE networks use radio wave frequencies that provide excellent coverage over a large surface area, with signals that can penetrate relatively dense materials. While Wi-Fi networks also use radio waves, their access points are designed for the short-range coverage commonly seen in homes or offices.
Even when you compare Wi-Fi 6 vs private LTE, the latter comes out on top in terms of performance, reliability and operational benefits. Private LTE offers faster transmission, higher bandwidth and better coverage, making it the better choice for enterprises that need:
- Reliable, high-speed connections to transmit ongoing streams of data from IoT devices.
- More control over roaming mobile devices to deliver uninterrupted handoffs between access point radios.
- Secure, scalable networks that limit access to whitelisted devices, even in locations that are far away from centralized IT.
Watch our Pre-Recorded Webinar on Private Networks Revolutionizing Manufacturing
Discover why more and more manufacturing outfits are turning to private wireless networks as an answer.
Watch Video
Benefits of Private LTE
.jpg?lang=en-US)
Across various industries, enterprises are increasingly considering how private cell networks can solve the problems introduced by unreliable connectivity. Developing a private network provides an exclusive LTE network in an uncrowded spectrum, and dedicated equipment increases device and data capacity.
Taking this approach also has the advantage of built-in controls not possible in public networks. Compared to public LTE or Wi-Fi networks, private LTE networks also offers better:
- Privacy: In a private LTE network, data never leaves the customer's network. This is especially important for tightly regulated industries, such as health care or finance.
- Security: SIM card security ensures that devices have a unique identifier on the network and are properly authenticated, ensuring tight control over the devices allowed on the network.
- Flexibility: Private LTE networks can be customized to meet an organization’s unique application needs.
- Capacity: Private LTE networks use either dedicated or shared spectrum, allowing organizations to tailor their infrastructure density based on their needs.
- Quality of service (QoS): Cellular technology provides improved QoS and data traffic prioritization over Wi-Fi, which allows business and mission-critical applications to function in situations when other networks are overloaded.
- Latency: Private LTE supports deterministic latency — the ability to set a fixed length of time for the transfer of data, which can be very important for use cases that require devices to be tightly synchronized.
- Resiliency: With private LTE, enterprise customers can deploy additional small cells for increased resiliency and uptime. If desired, they can also allow fallback to public LTE using the same cellular device.
- Mobility: In contrast with Wi-Fi, private LTE mobility, the hand-over between private LTE small cells, is seamless and comparable to that of public LTE.
- Cost: While the cost of an individual small cell is higher than an enterprise-grade access point, fewer small cells are needed to provide the same coverage as many Wi-Fi access points. With private LTE infrastructure, the cost for running cables, power and the maintenance of a larger number of nodes is significantly lower. For this reason, most see private cellular network cost savings over public networks.
Building a Private LTE Network
When planning to build and deploy a private network, enterprises have a number of options to consider before choosing their path forward. Each organization needs to weigh the associated costs against its specific business needs.

The Cost to Build Private LTE Networks
Without a clear understanding of your company’s intended use cases and network requirements, private LTE network costs can add up quickly. Depending on your approach, LTE network costs can include:
- Construction materials and labor for underlying infrastructure (including private LTE base stations)
- Purchasing and installing small cell radios
- Monthly charges for LTE services, which depend on the spectrum used
The total cost to deploy a mobile private network depends on a variety of factors, but the biggest difference comes from the spectrum your organization chooses.
Private LTE Network Providers
Enterprises can lease dedicated frequencies — by far the most expensive option. They also have the ability to lease Tier-2 CBRS connections from companies that own a PAL. The list of private LTE vendors that offer one of these options includes:
- AT&T
- Verizon
- Samsung
- Nokia
- Motorola Solutions
- Google Cloud
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
While there are definite benefits to paying for dedicated or Tier-2 CBRS network services, organizations also have the option of leveraging free Tier-3 access to CBRS frequencies.
How to Build a Private Network
Implementing a private LTE deployment requires three key steps.
First, Determine Your Connectivity Needs
The overall process starts by choosing the spectrum your network will use.
- Licensed spectrum. To set up a highly reliable private LTE network, organizations can choose to rent a dedicated part of the spectrum owned by a mobile network operator like AT&T or Verizon. Every country has unique laws that dictate how bands within the licensed spectrum can be used.
- Shared spectrum. Another way to create a private LTE network is via CBRS’s shared spectrum — more specifically by using Tiers 2 and 3. While a dedicated band can deliver better performance, shared spectrum offers a more affordable way to access the benefits of private LTE.
- Unlicensed spectrum. A private LTE network can be set up in an unlicensed band such as UNII-3, which is also used for Wi-Fi networks. While this can cost less than other options, unlicensed spectrums are less than ideal when it comes to performance due to higher volumes of traffic.
Set up the Core Network
Next, you’ll need to design and set up the core network architecture, which includes the LTE Evolved Packet Core (LTE EPC). The core network is made up of multiple nodes and designed with your organization’s mobility, security, authentication and traffic management needs in mind.
The EPC connects to both external networks and on-site base stations (called evolved NodeBs or eNBs), which serve as the central source of the private LTE signal.
Install Access Points
Lastly, you’ll need to install and connect LTE access points that provide sufficient coverage for your site and use case. LTE and 5G routers offer significantly wider coverage areas compared to WiFI access points, which makes them ideal for many industrial and commercial use cases. When selecting and installing routers, look for options with:
- Features that simplify deployment and management at scale.
- Fully integrated cellular solutions with Intelligent backup connectivity.
- Robust device security and secure edge computing capabilities.
Enterprises using the CBRS spectrum will also need to implement a Spectrum Access System (SAS) to assign frequency channels to CBRS access points.
Industries Adopting Private LTE
.jpg?lang=en-US)
There is an IoT revolution happening across industries as an increasing number of network-connected devices are being used in customer interactions and industrial operations. Private networks are well-suited to a range of use cases:
- Hospitals
- Office buildings
- Retail stores
- Shopping malls
- Construction sites
- Warehouses
- Industrial sites
- Farming operations
A private LTE network can handle all of the data that the devices in these network deployments generate. In the future, as machine learning and AI become even more prevalent, a private LTE network will provide the bandwidth these data-intensive programs require.
A private LTE setup can connect IoT sensors, cameras, autonomous equipment and drones on one network, unhindered by the limitations of a public network, making it a popular option in manufacturing, energy and transportation.
Private LTE is also becoming increasingly popular in the mining industry. An LTE network can cover a wide area, making it suitable for a mining operation spanning many square miles. Crucially, a private network is future-proof as it’s designed to handle the high-data requirements of a large mining fleet.
The same benefits are also helpful for global ports. A port with a private LTE network can ensure near-perfect uptime as well as consistent data transfer speeds. From docked ships to the cranes unloading them, a private network can cover an area that Wi-Fi can’t and ensure that everyone stays connected. When implemented in Rotterdam’s port, for instance, a private LTE network was able to provide 99.99% uptime.
Private LTE Deployments and Use Cases
When a company or organization needs to set up a localized network, and Wi-Fi is not an option, a private LTE deployment may be the perfect solution. As IoT continues its upward trend, LTE can support the inevitably heavy traffic loads, handling incoming data from tens of thousands of IoT devices.
LTE networks also have excellent penetration, reaching through buildings and other obstacles that may block a Wi-Fi signal. These capabilities are incredibly important for many of the data-intensive use cases that enterprises are using private LTE to realize.
.jpg?lang=en-US)
Whether an organization opts to use a licensed LTE network or to set up their own on a shared band — e.g. Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) — they can expect to save money and enjoy increased reliability over the public network. Private LTE networks will see increasing adoption for a wide range of connectivity needs, in both the commercial and consumer spaces.
Environmental Monitoring
Environmental monitoring is an incredibly valuable use case for industrial organizations, which often have mission-critical equipment deployed in remote locations with variable conditions. With remote management via a private LTE network, IoT devices can transmit millions of data points, that can then be analyzed and used to protect on-site staff, prevent unsafe conditions and sustain operations.
Real-time Security and Compliance Monitoring
In addition to environmental monitoring, organizations that operate remote sites can also benefit from IoT-enabled security and compliance monitoring. Real-time applications can leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) analytics to intelligently assess risks and react to minimize vulnerabilities, making private LTE especially valuable in industries with strict data security requirements.
Smart Automation and Predictive Maintenance
Using private LTE can allow enterprises to more feasibly implement predictive maintenance, especially at remote industrial sites where public networks are less likely to offer the needed coverage and bandwidth. With private LTE, IoT devices deployed at manufacturing facilities, agricultural sites and energy plants can use AI/ML applications to intelligently automate equipment usage, distribution and logistics, as well as identify safety or performance issues before a problem arises.
Other Use Cases
Data-intensive use cases are becoming increasingly important across retail, health care, manufacturing and even city planning. By providing better performance, reliability and security, private LTE networks enable advanced use cases that are transforming how the world around us operates:
- Augmented and virtual reality
- Intelligent visual inspections
- Theft prevention
- Real-time patient monitoring
- Personalized shopping experiences
Deploy Private LTE Based on CBRS with Digi
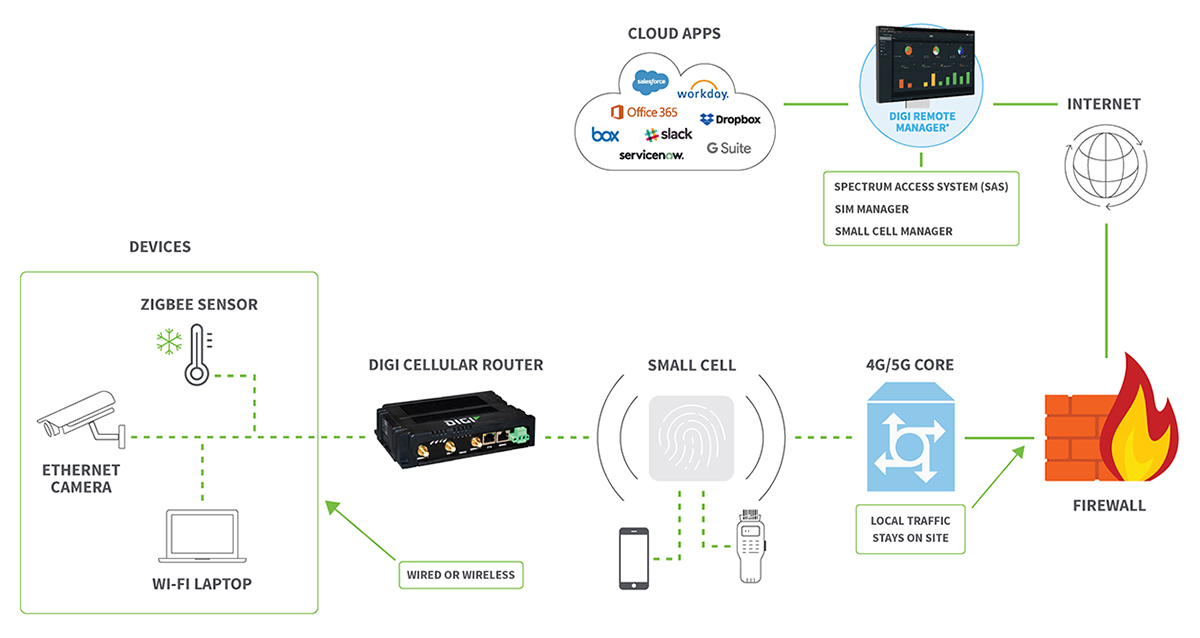
Whether an organization opts to use a licensed LTE network or to set up their own on a shared band, they can expect to save money and enjoy increased reliability over the public network. Private LTE networks will see increasing adoption for a wide range of connectivity needs, in both the commercial and consumer spaces.
As you explore how to build your own private LTE network, Digi International has the solutions and expertise to simplify your journey. Whether you need highly secure, reliable 4G and 5G cellular routers or a migration path to 5G, our teams can help you navigate all the options based on your business requirements and determine the best fit.
Learn more in our Private LTE solutions.
Next Steps