The manufacturing sector flourishes when it constantly seeks ways to optimize performance, and it’s never been easier thanks to IoT for operational efficiency. In fact, the Internet of Things (IoT) has opened up a new world of possibilities. IoT has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing operations by connecting various devices and machines to the Internet, enabling real-time data monitoring and analysis.
This blog will cover:
- Four IoT components in manufacturing
- Four examples of IoT devices in manufacturing
- Five key benefits of IoT on operational efficiency
Get Our eBook
Learn about Industry 4.0 technology
Download PDF
Four IoT Components in Manufacturing
The implementation of IoT in the manufacturing sector relies on several key components that work in tandem to create an interconnected and efficient ecosystem.
Sensors
These devices are embedded in machinery and production lines to collect real-time data on:
- Equipment performance data
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Humidity
Sensors act as the IoT system’s eyes and ears, providing the necessary data for analysis and decision-making.
Connectivity
Connected devices like cellular routers and embedded wireless modules provide the protocols and connectivity across device networks, and facilitate communication between sensors, devices, and systems. Connectivity can be achieved through various means, such as:
- Specialized industrial communication standards like cellular communication, Zigbee and LoRaWAN
- Cellular networks
- Bluetooth
- Wi-Fi

(Image Source)
Reliable and secure connectivity ensures data flows seamlessly from sensors to the central processing units.
Data Processing
Data is processed to extract meaningful insights. Data analysis can occur either.
- In the cloud, where hundreds of terabytes of data (and more) can be stored and analyzed
- At the edge, closer to the source of data collection, to enable quicker response times and reduced latency.
Advanced algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) techniques are often employed to process and analyze the data, identifying patterns and predicting potential issues before they arise.

(Image Source)
The User Interface (UI)
The UI connects human operators with the IoT system. A well-designed UI presents the processed data in a clear and actionable format, often through dashboards or mobile applications.
That way, operators can monitor the status of the manufacturing processes, receive alerts, and make informed decisions based on real-time information. An intuitive UI is essential for effective human-machine interaction, ensuring users can easily interpret data and respond promptly to anomalies.
Together, these four components form the backbone of IoT in manufacturing, enabling an intelligent, responsive, and efficient production environment.
4 Examples of IoT Devices in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, several IoT devices play crucial roles in boosting operational efficiency and productivity.
Smart Sensors
Smart sensors monitor several parameters, including temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration, and motion. For instance, temperature sensors can ensure that manufacturing processes that require precise thermal conditions remain within specified ranges.

(Image Source)
In contrast, vibration sensors can detect anomalies in machinery operation, signaling potential maintenance needs before a breakdown occurs.
Connected Machines
These machines have embedded sensors and communication capabilities, allowing them to transmit performance data and receive instructions in real time.
Examples include CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and 3D printers that can be remotely monitored and controlled, optimizing production schedules and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance.

(Image Source)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) and Robots
AGVs are used for material handling, navigating factory floors autonomously to transport goods between different stages of production. They rely on IoT technology to follow optimal paths, avoid obstacles, and communicate with other devices to ensure efficient workflow.

(Image Source)
Similarly, industrial robots equipped with IoT capabilities can perform repetitive tasks with high precision. You can also reprogram on the fly to adapt to changing production requirements.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices for factory workers are becoming increasingly popular as well when you invest in IoT for operational efficiency. These can include smart glasses or wristbands that provide real-time data and alerts directly to workers, improving safety and productivity.
Imagine factory workers wearing smartwatches or badges that track their activity levels, location, and even fatigue. This data can be fed into the employee scheduling app.

(Image Source)
Additionally, smart glasses can display assembly instructions, reducing errors and speeding up the learning curve for new employees.
Another example is environmental monitoring devices, which track conditions within the manufacturing facility to ensure a safe and compliant working environment. These devices can monitor air quality, noise levels, and other environmental factors and send alerts if conditions exceed safe thresholds.
Lastly, smart energy meters monitor and manage energy consumption in real time. These devices help manufacturers optimize their energy use, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact by providing detailed insights into energy patterns and identifying opportunities for savings.
5 Key Benefits of IoT for Operational Efficiency
Now, let’s dive into the key benefits of investing in IoT for operational efficiency.
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Real-time monitoring is a fundamental part of IoT.
By embedding sensors and connectivity solutions in machinery and production lines, manufacturers can continuously track the performance and condition of their equipment.
In the health industry, medical courier services would greatly benefit from IoT.
The medical manufacturing sector needs to deliver medical equipment and supplies on time and within budget to healthcare facilities, so IoT sensors can help track shipments and traffic conditions in real time to optimize routes and ensure timely delivery.

(Image Source)
These sensors gather data on various parameters and are transmitted to a central system for analysis. In return, the people managing the systems can immediately detect and correct anomalies and deviations.
Continuous monitoring ensures that the manufacturing processes run smoothly, minimizing downtime and boosting productivity. And in some cases, human intervention isn’t needed.
For example, if a sensor detects a machine operating at a suboptimal temperature, the system can automatically adjust the cooling mechanism to maintain the desired temperature. This level of control reduces the likelihood of defects and waste, ensuring that products meet quality standards.
To increase operational efficiency, combining the data from IoT sensors and machines with software for monitoring employees is a great idea.
This provides insights into how employees work and utilize the machines, thus allowing them to optimize workflows, identify bottlenecks, and allocate resources more efficiently. Moreover, this type of software can also help in quality assurance, helping ensure employees are adhering to safety protocols and potentially reducing accidents.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Traditionally, maintenance is performed on a fixed schedule or after a failure, which can be inefficient and costly. Unplanned downtime can financially hurt manufacturers as much as $260,000 per hour, costing the industry $50bn annually.
IoT-enabled predictive maintenance uses sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they happen. By analyzing trends and patterns in the data, such as increasing vibration levels or irregular temperature fluctuations, the system can predict when a machine is likely to fail and alert maintenance personnel.
A proactive approach allows maintenance to be scheduled at the most convenient times, reducing unplanned downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment. Predictive maintenance further lowers repair costs and minimizes the impact on production schedules.
3. Inventory Management
Smart sensors and RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags can be attached to raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods, tracking their location and status throughout the manufacturing process. The result? Better supply chain management.
This level of detail allows manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels. That way, you always have materials available when needed without overstocking.

(Image Source)
Automated inventory tracking eliminates manual stock counts and minimizes human error, leading to more accurate inventory records. IoT systems can also integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, providing real-time data that helps in better forecasting and planning.
For example, if the system detects that a particular component is running low, it can automatically trigger a reorder, preventing stockouts and production delays. This level of automation streamlines supply chain operations and improves order fulfillment rates.
4. Energy Management
Manufacturing facilities consume significant energy, and inefficient usage leads to high operational costs and a negative impact on the environment.
IoT-enabled energy management systems use smart meters and sensors to track energy consumption in real time across different machines and processes. This data allows manufacturers to identify energy-intensive operations and inefficiencies.
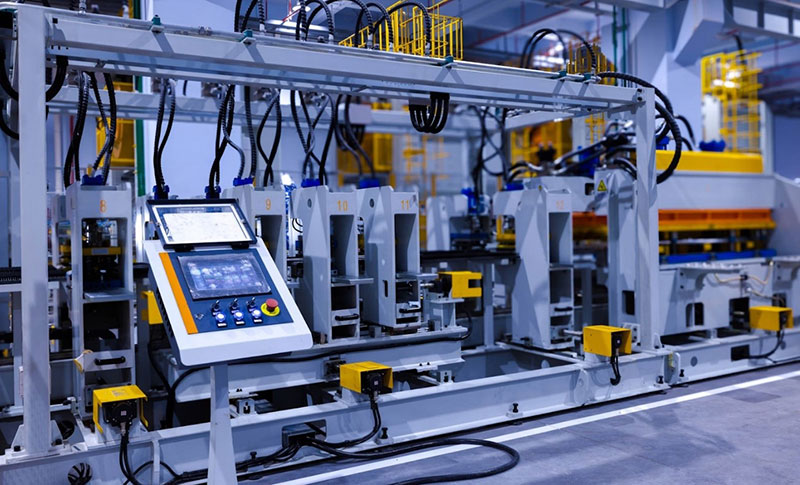

(Image Source)
By analyzing energy usage patterns, manufacturers can implement measures to optimize energy consumption, such as adjusting machinery settings during peak and off-peak hours or shutting down non-essential equipment when not in use.
5. Enhanced Communication
Using an employee app boosts efficiency in manufacturing by improving communication and making shift scheduling easier. These apps offer a single place for messages, announcements, and feedback, keeping everyone informed.

(Image Source)
They also help workers see and manage their schedules in real time, reducing conflicts and improving attendance. This leads to a more organized and productive workforce.
Overall, IoT is revolutionizing manufacturing, and it’s about time. For example, Harley-Davidson implemented IoT to reconfigure its production and improve the manufacturing facilities’ layout, reducing the time needed to create one motorbike from about three weeks to six hours.
Manufacturers are using this real-time intel to make smarter decisions, predict maintenance needs, and fine-tune production on the fly.
As these smart factories grow more complex, keeping an eye on all those connected endpoints becomes crucial. That’s where tools like endpoint monitoring software come in handy, helping maintain visibility across the entire network. The result? Less downtime, better quality control, and a severe boost of efficiency.

(Image Source)
How to Integrate IoT Devices Into Manufacturing
Different APIs can be used to integrate various IoT devices and systems seamlessly via an open-source API gateway. This approach ensures flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, allowing manufacturers to manage and route API requests efficiently.
By leveraging an open-source API gateway, manufacturers can facilitate secure and reliable communication between IoT devices and cloud services, streamline data flow, and implement custom traffic management policies.
This optimizes performance and significantly reduces downtime, ensuring smooth and continuous operations. Embracing open-source API is critical to unlocking the full potential of IoT in manufacturing, leading to more thoughtful and more efficient production environments.
Wrapping Up
As we’ve established, by investing in IoT for operational efficiency you, you can benefit from:
- Catching errors before they happen for better predictive maintenance and preventative quality control
- Greater efficiency through automation of complex workflows with minimal human intervention
- Overall cost reductions
Need an IoT solution? Digi is your IoT technology solutions partner. We build solutions customized to your unique specifications. Plus, we’ll natively integrate hardware, software, and peripherals — everything you need for your industrial or enterprise application.
Next Steps
About the Author
 Ryan Robinson is a blogger, podcaster, and (recovering) side project addict who teaches 500,000 monthly readers how to start a blog and grow a profitable side business on the IoT at ryrob.com.
Ryan Robinson is a blogger, podcaster, and (recovering) side project addict who teaches 500,000 monthly readers how to start a blog and grow a profitable side business on the IoT at ryrob.com.