The Internet of Things enables applications to connect and communicate with large numbers of wireless communication devices. It promises to power smart cities, utilities, manufacturing facilities, agricultural applications, remote industrial machinery and more. Any of these applications may use Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) network protocols.
For example, a smart city might use NB-IoT to monitor street lighting, utility meters and waste management systems across its municipality. A solar or wind farm could use Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) to monitor each of the units across the deployment. Industrial operations may rely on NB-IoT to remotely monitor all machines across distributed sites. In this blog post, we will answer the question, “what is NB-IoT?” and explore how it works and why it is important. Continue reading to learn why NB-IoT might be right for your application.
What Is NB-IoT?

NB-IoT stands for narrowband IoT. It is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology deployed on cellular networks over a limited range of frequencies. For IoT applications that don’t require lots of data communications or high-speed transmission and need to transmit over long distances, NB-IoT might fit your needs.
It can even send data indoors and underground while using very little battery power. This means it is a scalable, cost-effective and energy-efficient network option for devices even if they aren’t connected to the Internet.
Energy efficiency is an important aspect of NB-IoT. The NB-IoT protocol was designed from the ground up to power ultra-low power devices for a very long span of time. This means that expensive batteries for massive numbers of devices won’t need to be recharged or replaced very often.
Simply constructed NB-IoT chipsets mean lower component costs, as well. When you add the savings due to low data costs and longer time between battery replacements, NB-IoT delivers a lot of value in reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
Why NB-IoT?
NB-IoT has a range of benefits:
- Energy efficient — The built-in power save mode shuts down the NB-IoT module until an event trigger activates it, saving precious battery power
- Cost-effective — Low networking and data charges make an NB-IoT network an affordable choice for select applications
- Reliable connectivity over long distances — Narrowband IoT architecture is purposely designed to send small data packets over vast distances
From a range of smart city use cases such as smart city lighting to smart metering, as well as industrial, ecological and agricultural monitoring, NB-IoT supports a vast range of use cases.
How Does Narrowband IoT Work?

Long-term evolution, or LTE, is the next generation of technology that began with 4G and is designed to not “expire” with the rollout of the subsequent generation. LTE and NB-IoT pair well together.
What is NB-IoT in LTE? Initially specified in the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Release 13, NB-IoT technology operates in very narrow frequencies to communicate using existing GSM and LTE technologies. NB-IoT adopts the same frame structure as LTE. The NB-IoT bands in North America include B4 (1700 MHz), B12 (700 MHz), B26 (850 MHz), B66 (1700 MHz) and B71 (600 MHz). 3GPP defines 5G NR, NB-IoT, LTE and LTE-M for private wireless. The 3GPP Narrowband IoT standard was designed especially for low-cost and energy-efficient, indoor applications involving many connected devices.
NB-IoT supports simple devices with a very narrow bandwidth of either 180 kHz or 200 kHz. This narrowband IoT bandwidth means that the maximum data rate is around 250 kilobits per second. But a fast data rate isn’t necessary for narrowband IoT architecture. The specially designed sensors that collect information from the environment only share data in small packets to an NB-IoT base station.
Narrowband IoT is a cellular standard based LPWAN that operates on 4G and 5G bands. Narrowband IoT frequency bands are authorized and specially planned bands. NB-IoT frequency bands can be integrated with existing cellular network base stations making them more likely to be deployed. In other words, NB-IoT is supported by mobile providers around the globe.
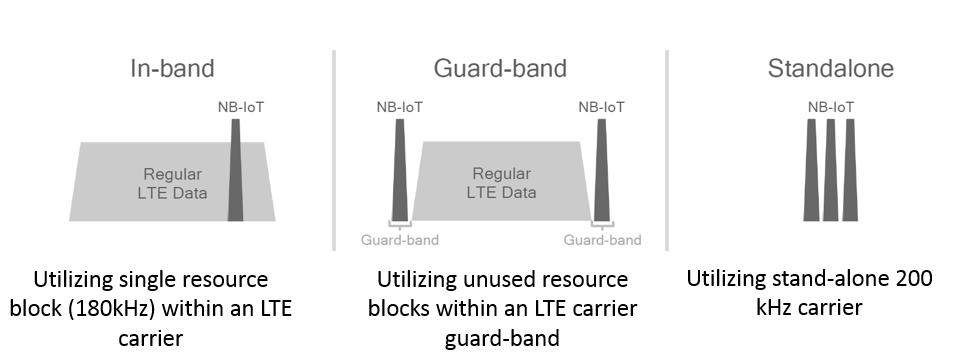
Deploying Narrowband IoT Technology
- In-band — Uses resource blocks in a normal LTE carrier
- Guard band — Uses unused resource blocks within an LTE carrier
- Standalone — Spectrum currently used by GSM EDGE Radio Access Network systems in place of GSM carriers when cellular services are not available
NB-IoT Availability
Operators in the U.S., many parts of Asia, the Middle East, Europe as well as Australia support NB-IoT. In fact, you can find NB-IoT networks in most countries around the world. Regions of the world that have larger GSM deployments than LTE may find it easier to support NB-IoT. In the U.S. and Mexico, major carriers have invested heavily in LTE-M, so they will probably continue to focus on developing that technology over NB-IoT. Carriers that don’t support NB-IoT include Orange in Europe and NTT DoCoMo in Japan.
5G vs NB-IoT

As mentioned earlier, 3GPP defined NB-IoT. It is also responsible for 5G and has made NB-IoT part of the 5G standard. In fact, NB-IoT and LTE-M comprise the only low power wide area (LPWA) standards that 3GPP plans to support.
5G is the fifth-generation mobile network and uses higher radio frequencies than previous 4G and earlier network generations. The millimeter wave frequencies that 5G uses allows it to transfer large volumes of data much faster. A major downside to millimeter wave technology is that its signal is easily disrupted by weather, trees and buildings.
NB-IoT cannot carry much data and it isn’t fast, but it excels at transmitting information over long distances and even through obstructions such as buildings. In other words, 5G and NB-IoT will coexist because NB-IoT is one of the only technologies that support cellular LPWA networks. Another related option is LTE-M. Note that the Digi XBee Cellular product family includes modules with both LTE-M and NB-IoT protocols built in, which enables developers to try both and identify the one that works best for their needs.

NB-IoT Cloud Potential
An NB-IoT cloud platform is typically part of the narrowband IoT architecture, designed to process services and send data to a business application. However, smart edge devices that enable an edge computing paradigm can reduce the need for a cloud-based architecture.
Multiple trials are underway to explore the cloud potential of NB-IoT. For example, Spain’s Sateliot plans to be the first satellite company to provide global IoT coverage with 5G. It recently announced plans to partner with AWS to build a cloud-native NB-IoT 5G service for its Low Earth Orbit satellite constellation. The satellites act as cell towers and provide global cellular outdoor coverage for NB-IoT devices. Experts anticipate that 5G for narrowband IoT via satellite will enable enormous global IoT adoption and be a key enabler for NB-IoT growth.
Narrowband vs. Wideband
Selecting the right connectivity option for your IoT solutions depends largely on the application.
Narrowband systems generally have lower data rates compared with wideband systems that support higher data rate transmissions. Narrowband is better suited to applications that need to communicate small amounts of data over large distances.
In a smart city, narrowband IoT works perfectly for device-to-device communication. Smart city infrastructure might include intelligent parking systems, smart meters or even pollution monitoring systems.
Experts anticipate that the explosive popularity of industrial IoT devices will create huge narrowband IoT market growth over the next several years. The growing NB-IoT ecosystem means utilities, energy and other important industries can create massive IoT solutions to better manage operations.
Important Industrial Narrowband Examples
- Remote asset tracking — Businesses can use NB-IoT to remotely trace, track, and monitor assets and receive status updates
- Sustainable agriculture — From moisture and pressure sensors to pH sensors, NB-IoT efficiently and cost-effectively help farmers continuously monitor and alert when soil conditions change
- Smart vending — NB-IoT-equipped smart vending machines alert service providers about empty vending machine items
- Gas leak detection — NB-IoT works perfectly for continuous monitoring of air quality and automatically sends alerts when levels surpass thresholds
When we use the term wideband, we mean solutions using higher frequencies. But high frequencies have a narrow wavelength and transmit over shorter distances than narrowband. When an application requires voice or video transmissions, look to wideband. Think about wideband as the right solution in an IIoT environment where fast, accurate data transmission is essential for things like collision avoidance systems.
Industrial Applications Best Suited for Wideband
- Smart retail — Wideband works great for hands-free retail such as in an unmanned grocery store where customers can pick up items and receive additional product information or special offers
- Location-based services — From indoor mapping in places like airports and patient tracking in hospitals to bike sharing in cities, wideband has a precise ranging ability
- Secure building access — Through wideband-powered smart sensors, it is possible to automatically open doors to secure buildings with nothing more than a smartphone or watch
NB-IoT Security

As IoT device growth accelerates, digital security becomes a bigger concern. This is especially true as critical infrastructure such as energy and utility operations adopt NB-IoT for smart sensor communication. NB-IoT was purposely developed for reliable building penetration with minimal energy requirements over long distances. But what about security?
Because it is based on the LTE technology framework standardized by 3GPP, NB-IoT uses the same security features as LTE. Therefore, NB-IoT encryption means that any transmitted data gets encrypted using standard LTE encryption. Additionally, reciprocal authentication and secure key generation add up to a high level of security. And because of its standards alignment, NB-IoT can support current and upcoming security features designed for the entire cellular ecosystem. Note also that Digi XBee NB-IoT solutions include the built-in Digi TrustFence® security framework, which ensures authentication, and protected hardware and network ports.
Benefits of NB-IoT
Narrowband IoT and the NB-IoT market may grow globally to over 14 billion by 2030. Several key factors contribute directly to this growth. And for good reason. As the world looks to the promise of IoT to make our operations safer and more cost-efficient, NB-IoT fills the requirements.
Efficiency of Power
One of the key factors contributing to the NB-IoT market growth is the increasing demand for low-power wide area networks. These networks are in-demand in a variety of industries that require reliable connectivity inside buildings without using much power. Sometimes it is because monitoring devices are located on machines or in areas difficult to service. Other times, power efficiency dictates if connectivity makes sense financially.
The main reason that NB-IoT is so power efficient is that it has a built-in power-saving mode that sets IoT devices into a low-power mode and only wakes them up for short periods of time when receiving data or sending status updates. When it does wake to transmit data, NB-IoT greatly minimizes power consumption due to the simplified data transmission method and lower data rate it uses. As a bonus, using the power-saving mode dramatically extends IoT device battery life without impacting the operation of the device. In fact, NB-IoT sips so little energy that a single battery can power it for up to 10 years.
Financial Savings
NB-IoT provides financial savings in several ways. First, because NB-IoT has few complex waveforms, it uses less power. Second, an NB-IoT chipset costs less because it is simpler to manufacture. Third, reliable Narrowband IoT module connectivity improves overall dependability so operators can confidently control quality. Finally, NB-IoT connections usually cost less than traditional cellular connections. This really makes a difference when an operation requires many connected devices.
For example, deploying smart metering infrastructure using NB-IoT costs significantly less because utilities can deploy battery-powered meters that don’t need an expensive cellular connection. In fact, according to RF Page, Narrowband IoT devices can reduce energy usage by up to 90 percent.
Reliable Network for Users
What do autonomous vehicles and healthcare monitoring devices have in common? They both require reliable connectivity. That’s where NB-IoT shines. NB-IoT connections have a network availability of 99.999 percent making them up to ten times more reliable than traditional cellular networks.
In the automotive industry, autonomous driving requires large numbers of cars to communicate with other cars, traffic lights, and pedestrians without using a lot of bandwidth. In this use case, safety dictates extreme reliability.
In healthcare, everything is designed with reliability in mind, especially patient health monitoring. In the case of remote patient monitoring, heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature readings can get reliably shared with health centers.
Potential for Wider Deployment
According to market projects for Narrowband-IoT over the next several years, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) by 2030 is an astounding 69 percent. This projection is based on rising demand. The signals pointing to this growth include everything from increased R&D investments by solution providers to expanded digitization and automation in manufacturing.
Another emerging trend is the growing interest in satellite-based 5G services. With 5G NB-IoT moving beyond terrestrial networks, the farming industry could tap into satellite GPS tracking to monitor livestock. In agriculture, satellite-powered wireless networks could help farmers monitor everything from temperature to humidity.
As promising as it sounds, NB-IoT limitations remain. As the number of devices in large-scale deployments increases, device configuration and data volume become important issues. Operations teams must have the tools necessary to manage large-scale device and data security and privacy. Additionally, alternate technologies to NB-IOT like SDR and the lack of standardized IoT regulations has an impact on the narrowband internet of things (NB-IoT) growth.
Worldwide Reach
Although North America leads the NB-IoT market and will likely dominate by 2031, the Asia Pacific region is forecasted to experience incredible narrowband-IoT market growth. An increase in urbanization means increasing demand for technological development to improve the standard of living. For example, in Asia, China, Singapore and Thailand created huge Narrowband IoT applications. In China, more than 100 million NB-IoT connections enable intelligent fire suppression infrastructure. A Chinese company connected 30 million customers to an NB-IoT gas and water metering system making it the world's largest gas and water metering provider.
NB-IoT Applications

NB-IoT networks continue to address a wide range of applications that are reshaping entire industries around the world. NB-IoT networks support connectivity, remote monitoring and data insights. As deployment dramatically expands, the energy-saving features of NB-IoT will help reduce emissions. Here are a few of the most important applications.
- Kiosks and digital signage: NB-IoT supports the full breadth of connected self-service applications today, from ATMs and information kiosks to digital signage and lottery systems.
- Agriculture: From soil and moisture sensors for irrigation to water level sensors in water tanks, agricultural applications are some of the most active use cases for NB-IoT today.
- Smart cities: Connected cities today are using smart technology to reduce emissions, improve air quality, and improve connectivity and mobility services for their citizens. NB-IoT supports a wide range of use cases from smart building technology to city lighting and V2X (vehicle to everything) communications that improve safety for its citizens.
- Healthcare: NB-IoT technology provides several advantages for healthcare applications. Examples include remote patient monitoring through medical devices such as heart and blood pressure monitors and tracking of medical equipment in hospitals.
- Automotive: Growing demand for autonomous and connected vehicles is helping to drive growth in NB-IoT because it can be incorporated into infotainment, telematics, and vehicle diagnostics systems.
- Transportation: Connected systems like smart parking systems and electric vehicle charging stations can utilize NB-IoT networks, as can public transit maintenance systems.
- Logistics: NB-IoT can help smart factories and supply chain applications to integrate intelligence across operations with asset tracking, temperature monitoring rapid reporting.
- Home and building automation: Remote management of household appliances, smart building applications like HVAC systems and smoke and fire sensors are excellent use cases for NB-IoT.
NB-IoT is also used in industrial settings for asset tracking, inventory management, process optimization and machine performance monitoring.
Digi NB-IoT Solutions
 When selecting NB-IoT solutions, look for a partner that can provide more than just hardware. Large-scale implementations require an end-to-end solution that enables remote monitoring and management and regular security updates. Digi offers deep expertise and ready-to-deploy solutions so you can install, manage and support an NB-IoT network at any scale — anywhere.
When selecting NB-IoT solutions, look for a partner that can provide more than just hardware. Large-scale implementations require an end-to-end solution that enables remote monitoring and management and regular security updates. Digi offers deep expertise and ready-to-deploy solutions so you can install, manage and support an NB-IoT network at any scale — anywhere.
Digi's flagship NB-IoT offering is in the Digi XBee® 3 Cellular family of embedded wireless modules. The Digi XBee 3 Global and Low-Power LTE-M/NB-IoT modem provides compact, flexible cellular connectivity for IoT devices and gateways. This cellular module is FCC and carrier end-device certified for fast integration in low-power wireless applications in a wide range of regions worldwide.
The smallest end-device certified modem for cellular networks, this module supports both LTE-M and NB-IoT networks, and is suitable for a massive range of use cases from wearables to industrial robotics. It is easy to configure test, deploy and manage with Digi XBee Studio® and Digi Remote Manager®, and integrates the Digi TrustFence® security framework. Additionally, the module offers NB-IoT MQTT support as well as MicroPython programmability and Bluetooth® Low Energy for beaconing and connecting to Bluetooth sensors.
Additional Digi NB-IoT offerings include the Digi Connect® IT Mini console server — a secure and affordable solution for isolated remote IT devices — and the Digi CORE® plug-in LTE modem for scalable cellular connectivity.
NB-IoT Technology Barriers
NB-IoT is a promising technology with many great use cases. However, across the world, NB-IoT faces several challenges. Compared to LTE-M, NB-IoT has a low data rate and is not ideal for idle devices. Also, it doesn’t support Voice Over LTE, so it cannot transmit speech.
Financially, NB-IoT doesn’t always make sense, either. Deployments of less than 10,000 connections may not provide an adequate return for service providers. Furthermore, organizations such as utilities and governments require long planning periods before committing to an installation. Although operationally cost-efficient, the initial investment costs to acquire spectrum, licenses and services may prohibit wider deployment.
For these reasons, Digi XBee 3 Global LTE-M/NB-IoT module offers a complete, ready-to-deploy solution that eliminates many of the barriers, and helps to dramatically reduce many of the costs associated with development and certification.
Digi Offers Networking and IoT Solutions for All Your Needs
NB-IoT is an exciting networking technology with many current and promising future applications. And although it is cost-efficient and reliable, getting started with an NB-IoT design can be challenging without the right partner. Digi has been designing and building IoT devices and services since 1985. Digi provides complete hardware and software solutions, including a sophisticated platform for remotely monitoring your device deployments.
Best of all, the experts at Digi Wireless Design Services can help you at any and every step along the way. This team of talented engineers can consult with or augment your team as you design, develop and deploy your solution, and can provide ongoing monitoring and management of your deployment.
Ready to take the next step with your NB-IoT projects?
Next Steps